3D Printing
Introduction.
The 3D printing process builds a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design (CAD) model, usually by successively adding material layer by layer, which is why it is also called additive manufacturing, unlike conventional machining, casting and forging processes, where material is removed from a stock item (subtractive manufacturing) or poured into a mold and shaped by means of dies, presses and hammers.It is also known by the name of rapid prototyping
Type of 3D printing-
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Fused deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
- Electronic Beam Melting (EBM)
- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
- Binder Jetting (BJ)
- Material Jetting (MJ)
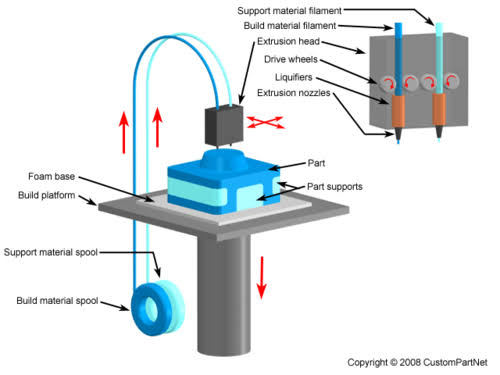
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Technology fdm-printing FDM is a 3D printing process developed by Scott Crump, and then implemented by Stratasys Ltd., in the 1980s. It uses production grade thermal plastic materials to print its 3D objects. It’s popular for producing functional prototypes, concept models, and manufacturing aids. It’s a technology that can create accurate details and boasts an exceptional strength to weight ratio. Before the FDM printing process begins, the user has to slice the 3D CAD data (the 3D model) into multiple layers using special software. The sliced CAD data goes to the printer which then builds the object layer at a time on the build platform. It does this simply by heating and then extruding the thermoplastic filament through the nozzle and onto the base. The printer can also extrude various support materials as well as the thermoplastic. For example, as a way to support upper layers, the printer can add special support material underneath, which then dissolves after the printing process. As with all 3D printers, the time it takes to print all depends on the objects size and its complexity. Like many other 3D technologies, the finished object needs cleaning. Raw FDM parts can show fairly visible layer-lines on some objects. These will obviously need hand sanding and finishing after printing. This is the only way to get a smooth, end product with an even surface. FDM finished objects are both functional and durable. This makes it a popular process for use in a wide range of industries, including for mechanical engineering and parts manufacturers. BMW uses FDM 3D printing, as does the well-known food company Nestle, to name just a couple.
Software Used
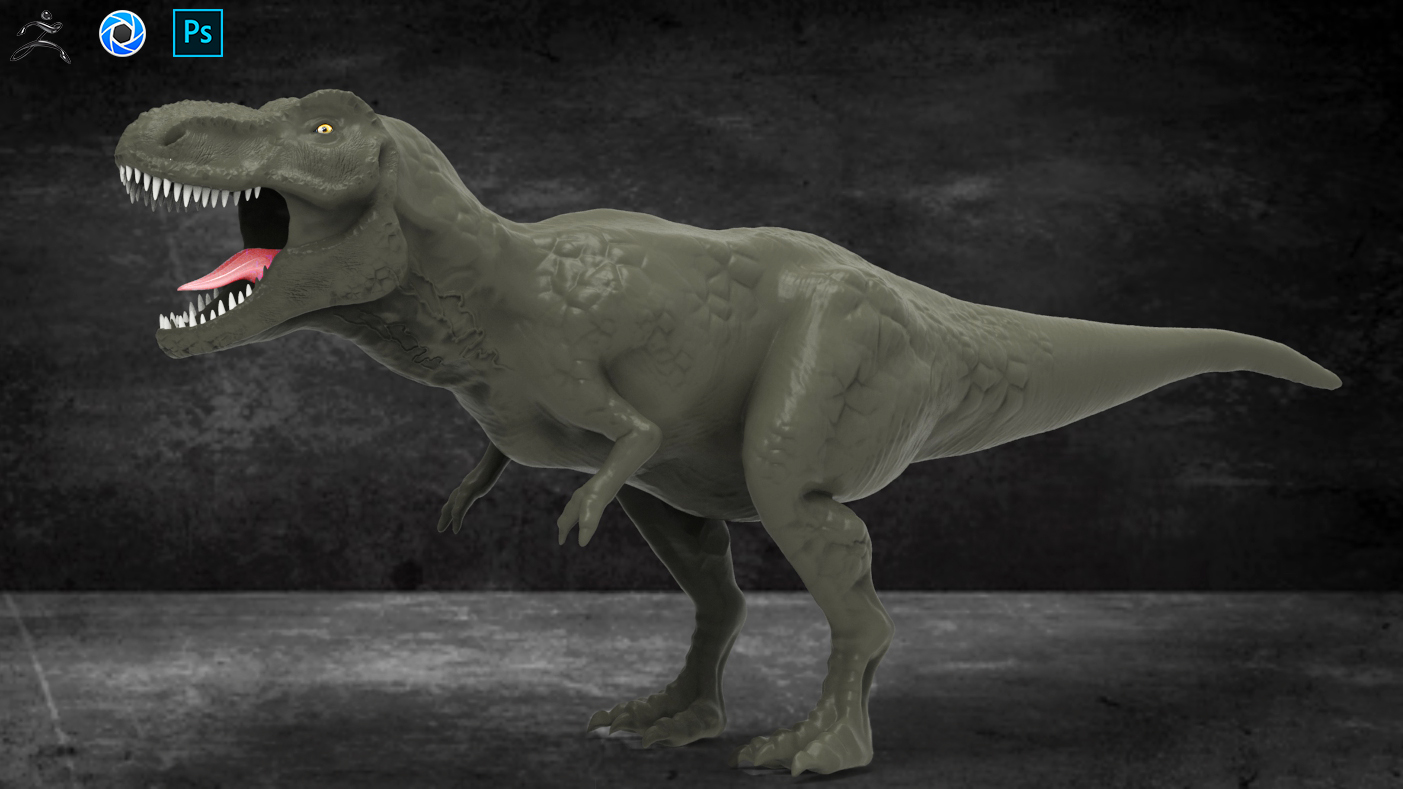
While doing this assignment I have made 3d Model in Zbrush and Imported in Idea maker.
Procedure
Step 1:Create 3D model in any CAD software and Export in .STL format.My model was build in Zbrush.

Step 2:Import .STL file in Idea Maker.
Step 3:Use tool to Scale, Positon and set supports for the model.
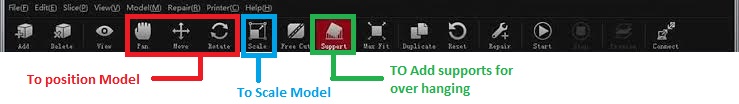
Step 4:Click on 'Start' and select Printing speed to generate 'G Codes'.
Step 5:Transfer 'G Codes' to 3D printing Machine.
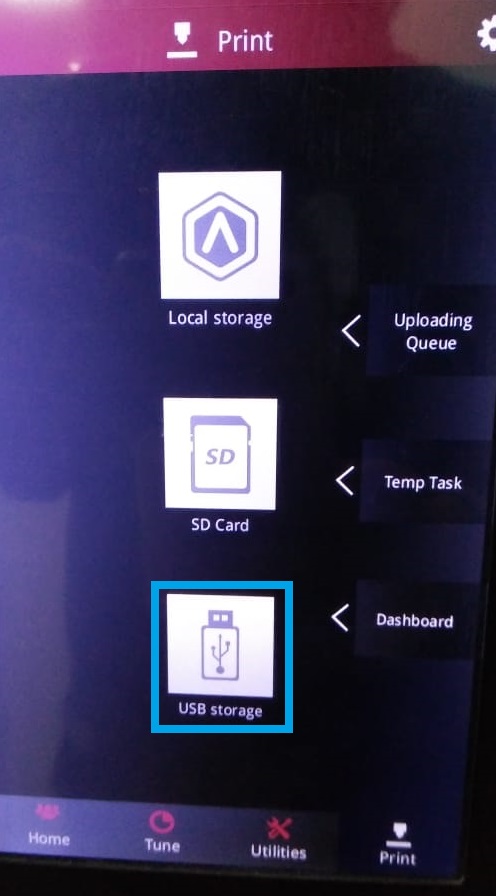
Step 6:Go to Print and browse the 'G Code' file.
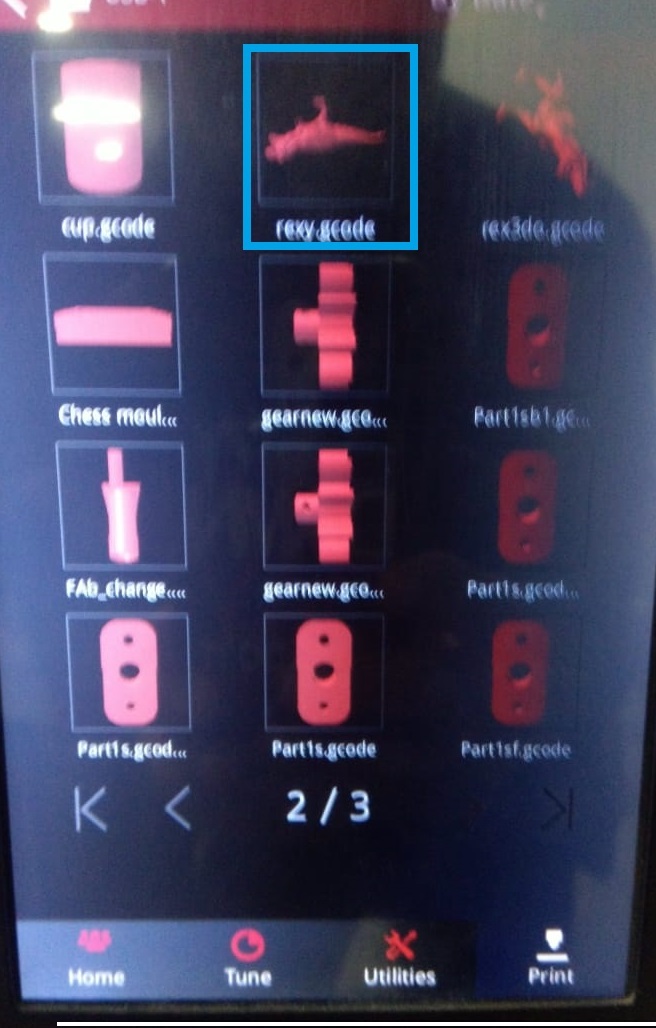
Step 7:Start Printing.
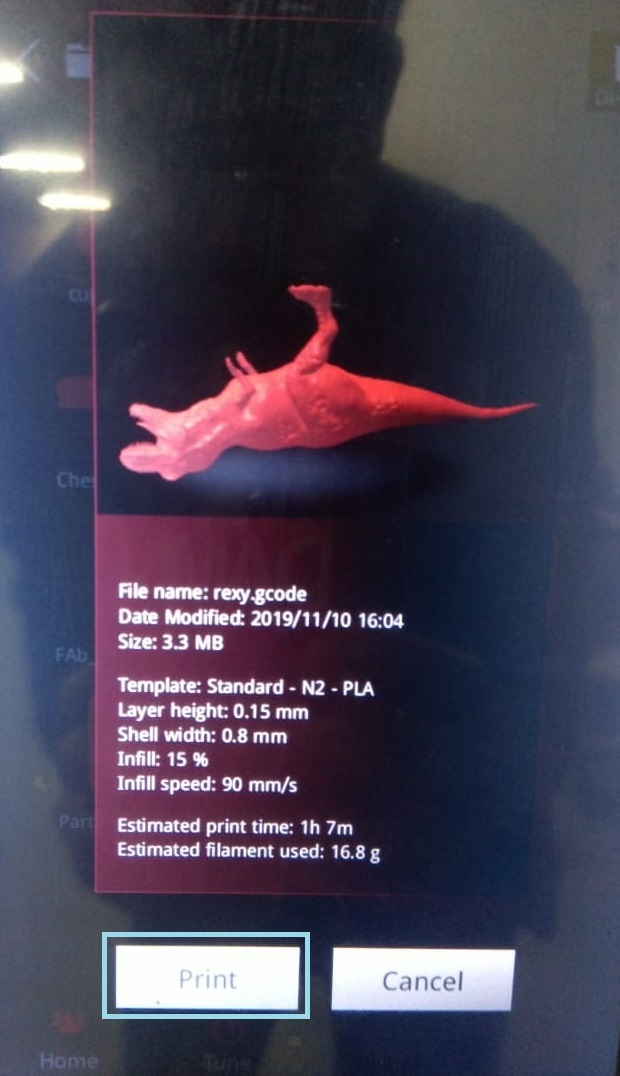
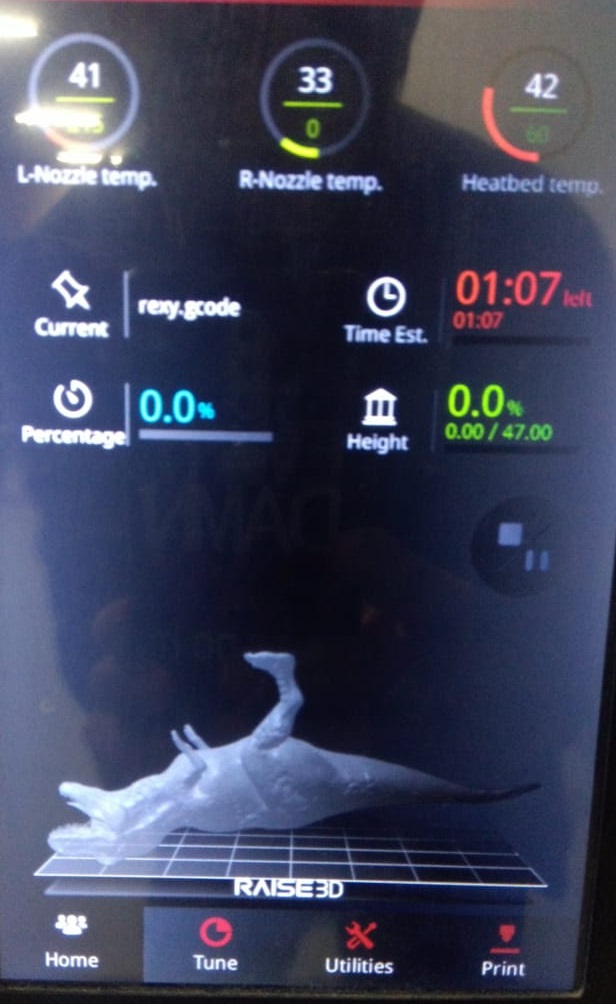
Step 8:Finished Product.
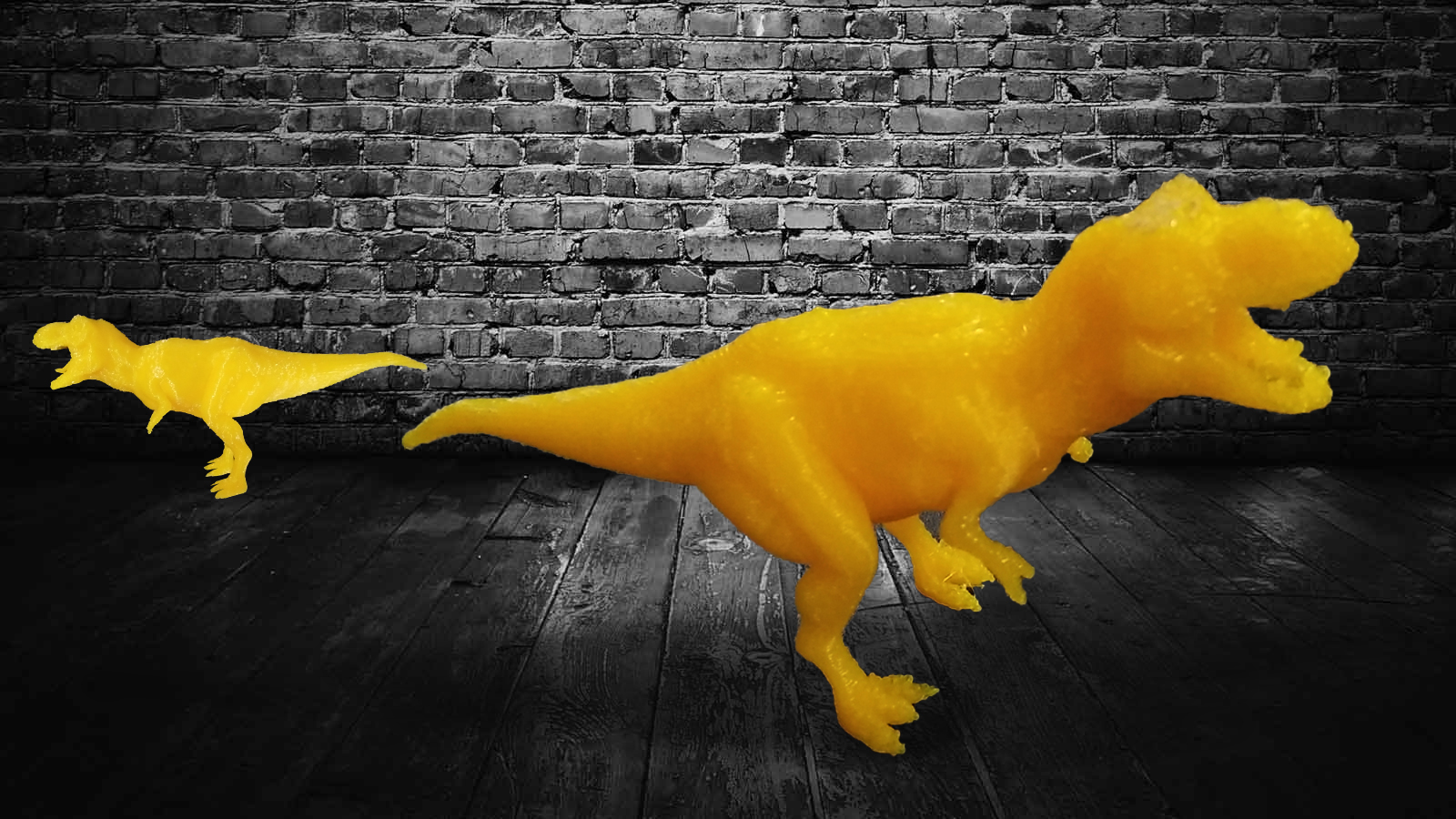
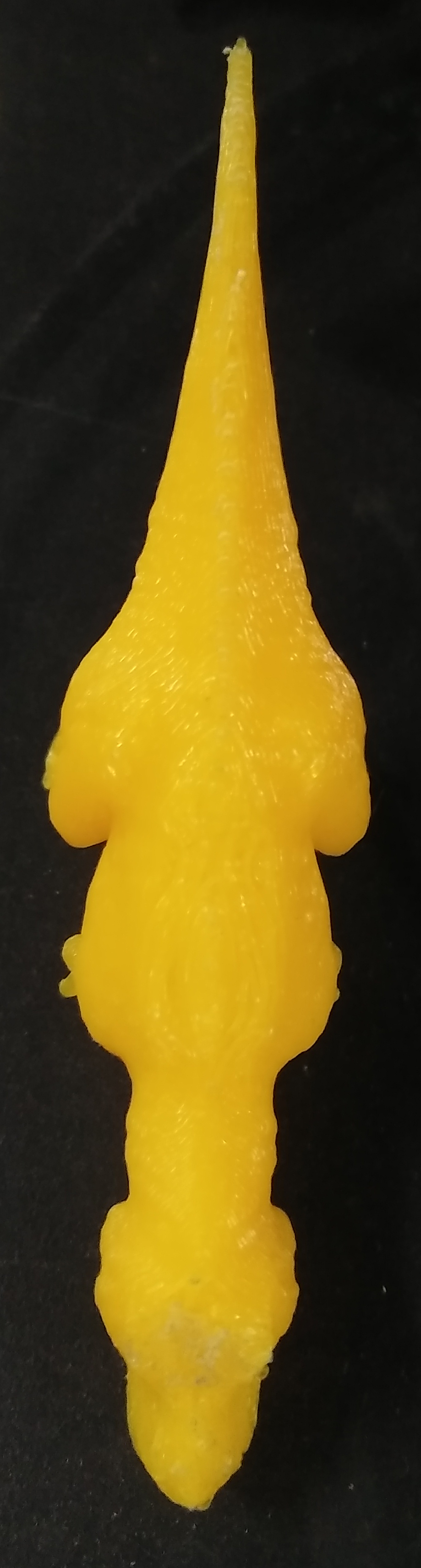


-------------------------------------End of Assignment---------------------------------------
