|
Funding Agency:
RDSO, Lucknow
Investigators:
-
Dr A. Chawla
-
Dr S. Mukherjee
Other Collaborating Agencies:
Project Objective:
In earlier phases of this project we have developed FE models of the
rail and have analysed it for vertical, vertical eccentric, lateral
and for combination of the individual loading. Initially, loading
was considered to be due to only one wheel and the effect of
multiple wheels was not considered. Subsequently, in phase III of
this project we had carried out analysis for multiple wheels (axles)
on a rail. In addition, experiments had been conducted at RDSO to
validate the results of the FE models. Models for different rail and
different load combinations have been analyzed and reported earlier.
However, the analysis so far has been limited to static loading and
the likelihood of fatigue failure has not been considered so far. In
this phase of the work, we are analysing the rail for likelihood of
fatigue failures due to rail bending. In this phase, fatigue
analysis is being carried out. A local stress strain approach to
estimate the stress based fatigue life as well as chances of crack
initiation and propagation has been carried out.
Highlights of the work:
The main contributions of the current study can
be summarized as follows:
-
The current design procedure for the stress estimation in the rails
has been critically evaluated.
-
FE models have been developed for the rails. These have been
validated against the experiments suggested by us and conducted at RDSO.
-
FE models have been developed for different rail – wagon
combinations.
-
Fatigue analysis methodology has been extensively studied and a
procedure has been suggested for estimating the fatigue life of the
rails.
-
A methodology has been suggested for deciding the wheel flat limits
for safe operation.
-
An action plan for the future has been worked out to develop
a methodology for the finalization of the maximum tonnage on a rail
/ track.
A finite element model has
to be developed carefully to obtain accurate solutions and there is
currently no procedural method for establishing a FE model. If the
geometry is known accurately, the issue is to determine the maximum
size of elements that yields sufficient accuracy. Refining the mesh
further consumes engineering time, storage space and computer run
time without any added accuracy benefits. Additional decisions have
to be made in specifying the boundary conditions and determining
material properties to be input. We have tried to establish a
methodology for ascertaining parameters relevant to FE analysis of
rails and wheels. Some typical snapshots of the FE models are
given below:
Cross
section of the FE model of the rail
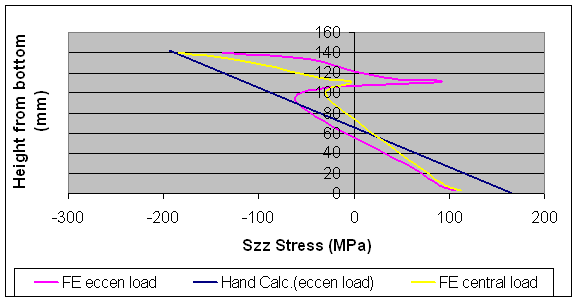
|