Photonic Biosensing
Photonic crystals are periodic structures with varying dielectric constants whose period is comparable with the wavelength of light.
These structures can confine light within a small volume and finds applications for sensing purposes. Guided Mode Resonance (GMR) structures have gained much
attention from many photonic crystal structures due to their simplicity of fabrication, cost-effective operation, label-free detection, and high sensitivity.
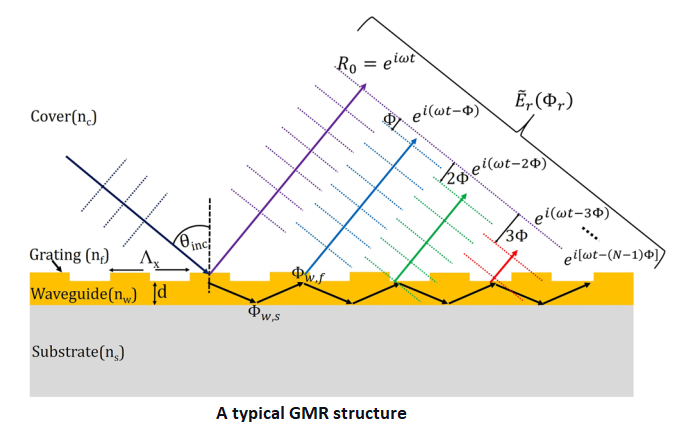
GMR structures consist of a low refractive index substrate layer and, on top of that, a high refractive index waveguide layer and a grating layer. When light is incident
on the grating layer, it diffracts into many orders. Under the specific phase-matching condition, one of the diffracted orders guides into the waveguide layer. As the wave
is guided, it diffracts whenever it encounters the interface of the grating layer and the waveguide layer. These diffracted waves interfere with the zeroth diffracted order,
and is reflected. This resonance condition manifests as a reflection peak in the reflection spectrum. Whenever the refractive index of the background changes, there is a
shift in the resonance peak. This feature of the GMR is used for sensing purposes. GMR is a structure-dependent device whose resonance wavelength can shift according to the
variations in the height and period of the grating, height of the waveguide, and material of waveguide and grating. It also depends on the wavelength of incident light used,
its polarization and the incident angle. Hence, for a particular sensing application specific structure can be fabricated accordingly
For the application of GMR as a biosensor, a linker is attached to the surface of GMR which can recognize the analyte or the target biomolecule. When the target molecule gets
attached to the surface the effective refractive index of the structure changes and as a result the reflection peak changes to a new value. From the change in reflection peak
the sensitivity of the structure can be determined. The sensitivity is defined as the change in the measurand to change in the refractive index. The measurand can be wavelength,
angle of incidence, phase, or intensity. Hence different detection schemes namely wavelength, angle of incidence, phase and intensity detection can be employed for sensing
application using GMR.
Publications
Sahoo, P. K., Sarkar, S., & Joseph, J. (2017). High sensitivity guided-mode-resonance optical sensor employing phase detection. Scientific reports, 7(1), 1-7.Joseph, S., Sarkar, S., Khan, S., & Joseph, J. (2021). Exploring the Optical Bound State in the Continuum in a Dielectric Grating Coupled Plasmonic Hybrid System. Advanced Optical Materials, 9(8), 2001895.
Joseph, S., Sarkar, S., & Joseph, J. (2020). Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon-Polariton Sensing at a Flat Metal-Analyte Interface in a Hybrid-Configuration. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12(41), 46519-46529.
Sarkar, S., Poulose, S., Sahoo, P. K., & Joseph, J. (2018). Flexible and stretchable guided-mode resonant optical sensor: single-step fabrication on a surface engineered polydimethylsiloxane substrate. OSA Continuum, 1(4), 1277-1286.
Sahoo, P. K., & Joseph, J. (2013). Optical diode using nonlinear polystyrene ring resonators in two-dimensional photonic crystal structure. Applied optics, 52(34), 8252-8257.