Latest Research
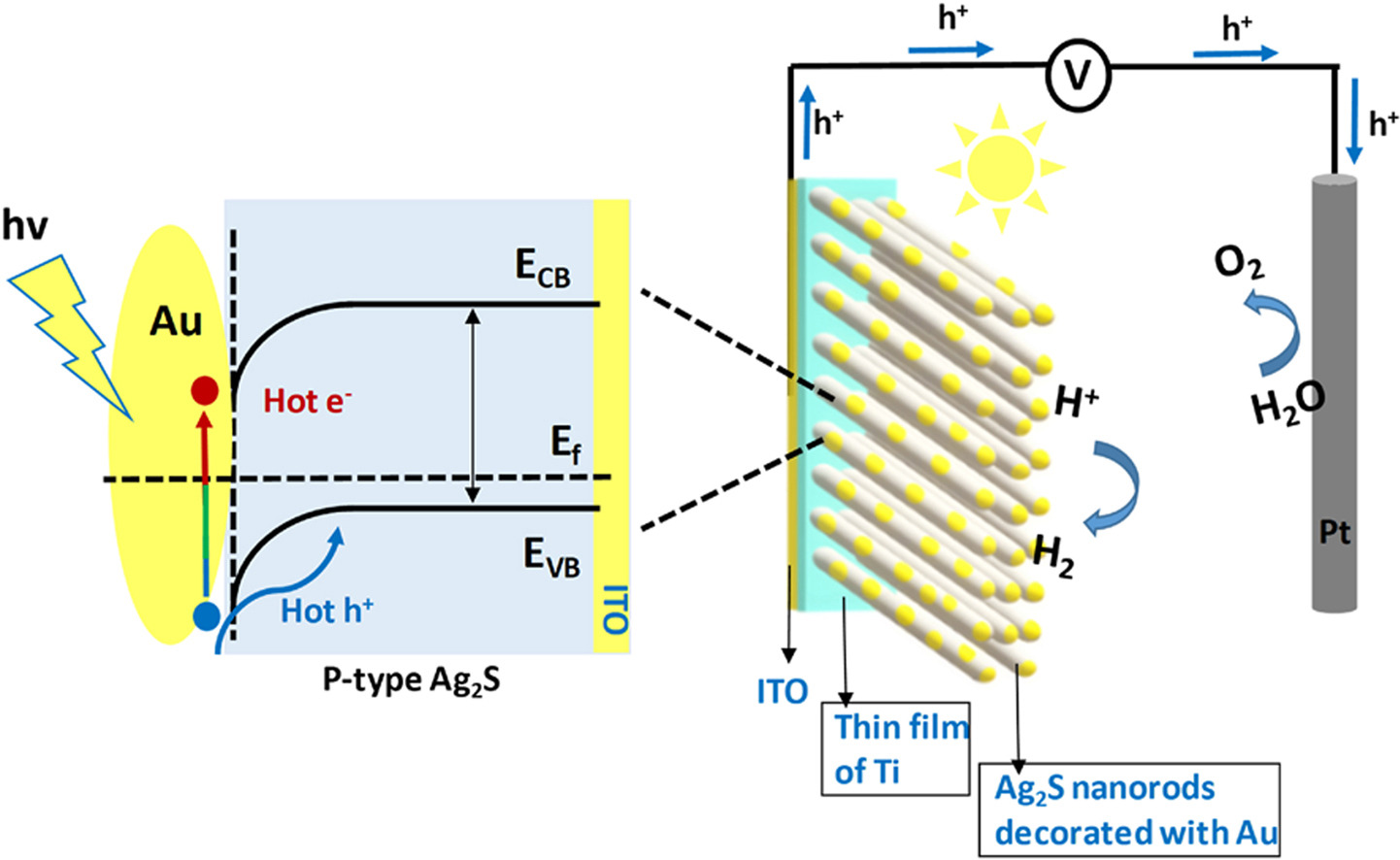
"Surface plasmonic hot hole driven Ag2S/Au/Al2O3 photocathode for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting performance."
- Ag2S/Au/Al2O3 photoelectrode was fabricated for superior photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting response.
- The superior PEC response may be ascribed to the synergic effect of plasmonic Au nanoparticles and the tilted Ag2S nanorods.
- The theoretical simulations based on finite difference time domain (FDTD).
- Ag2S nanorods and shed light on designing hybrid hot hole harvesting semiconductor nanostructures for the next generation photoelectrodes.

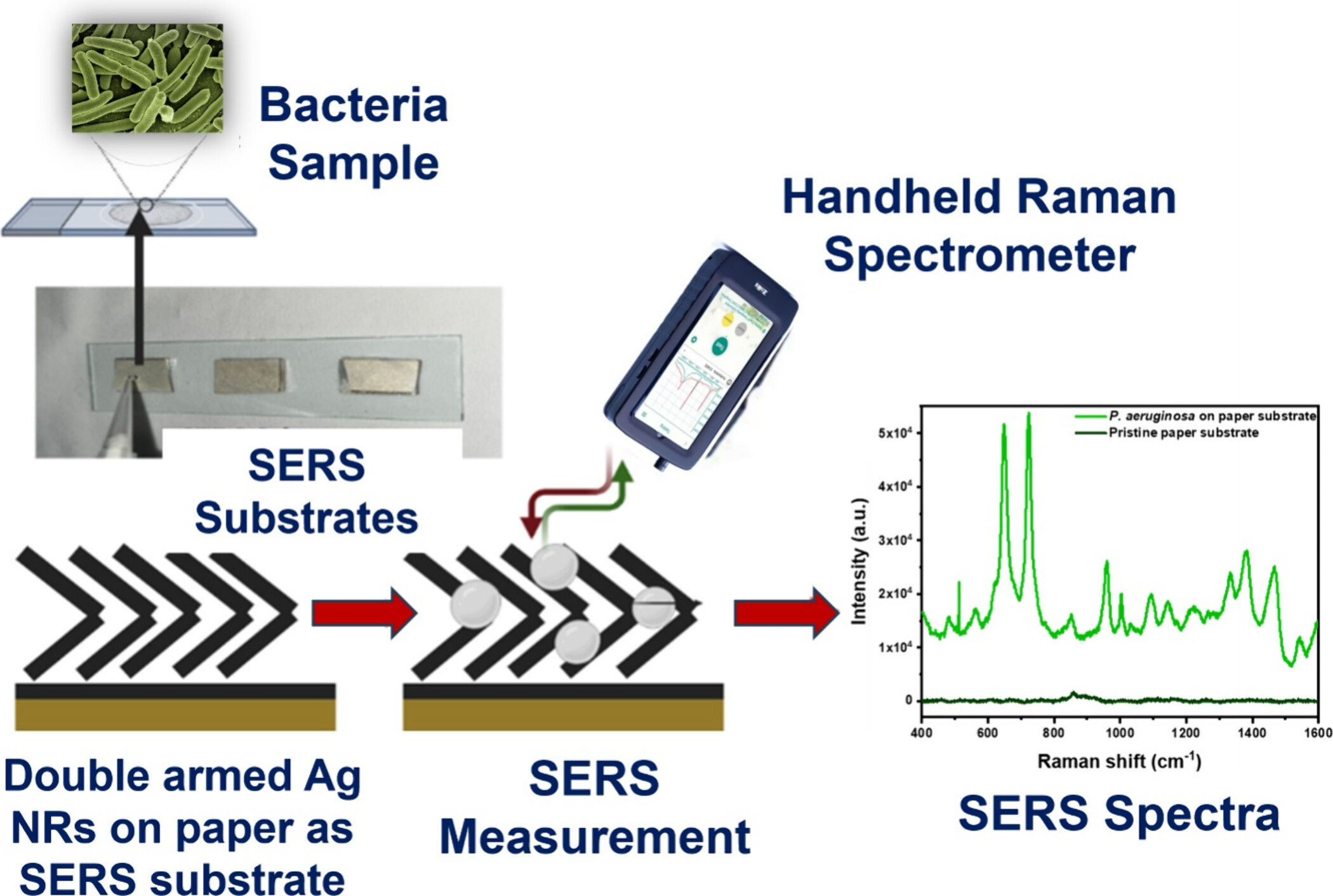
"Affordable Paper-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates Containing Silver Nanorods Using Glancing-Angle Deposition for Nosocomial Infection Detection."
- An excellent surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate offers exceptional signal enhancement and amplification while boasting a substantial surface area.
- The porous and fibrous nature of the paper-based substrate provides high roughness and surface area and hence enhances the plasmonic effect.
- To determine its applicability in public health, nosocomial-infection-causing bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus were detected.
- A separation between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria was observed using this substrate, showing immense potential in detecting biomolecules.
"Material Properties of n-Type β-Ga2O3 Epilayers with In Situ Doping Grown on Sapphire by Metalorganic Chemical Vapor Deposition."
- In situ, Si-doped heteroepitaxial Ga2O3 layers are grown on c-plane sapphire by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition.
- The X-ray diffraction peaks of the doped Ga2O3 epilayers shows ß-phase of Ga2O3 ,and full width at half maximum of Ga2O3 crystallinity is decreased at a Tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) molar flow rate of 2.23 × 10−7 mol min−1 but increased with higher flow rates.
- To increase Si dopant activation, Ga2O3 growth temperature is raised to 875 °C.
- The result suggests a higher growth temperature can contribute to a greater probability of Si substitution on Ga lattice sites.
- The results are compared with theoretical Density Functional Theory studies.


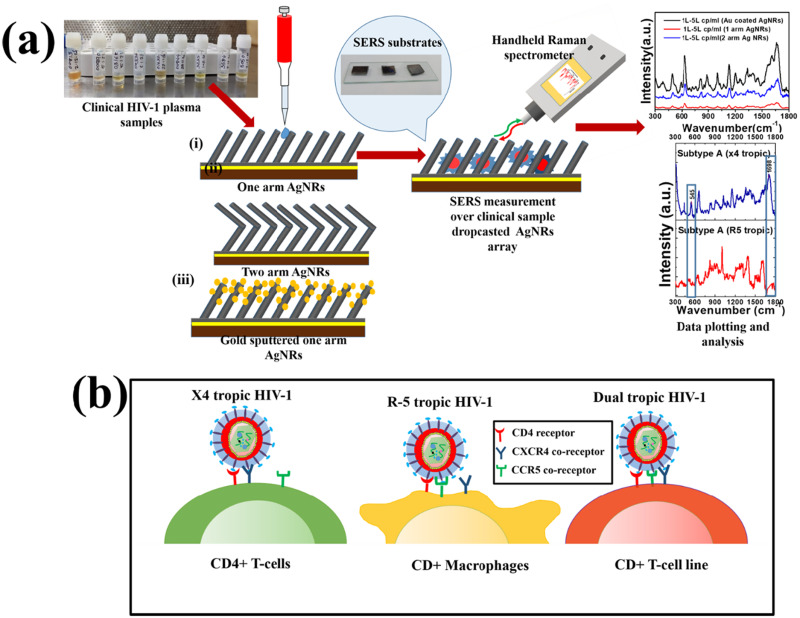
"A SERS based clinical study on HIV-1 viral load quantification and determination of disease prognosis"
- Detection and prognosis of HIV positive clinical samples using SERS..
- Clinical samples of seven different viral load ranges detected.
- 3 different highly sensitive SERS substrates fabricated using GLAD.
- Distinction of HIV-1 subtypes based on tropism using SERS.
- Theoretical studies done using RCWA simulations and PCA.

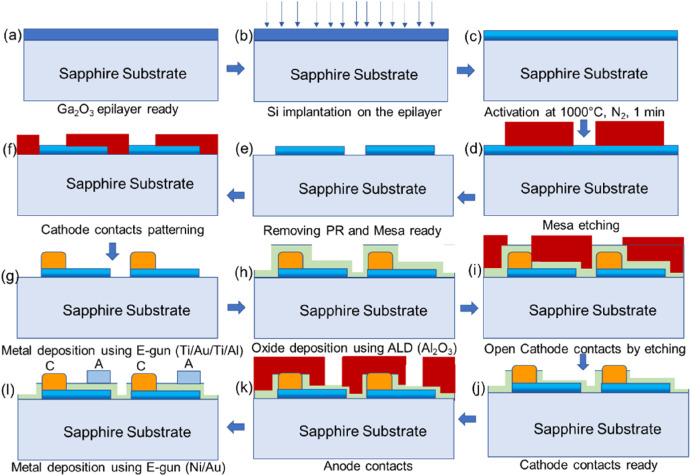
"Metal-insulator-semiconductor type diode based on implanted β-Ga2O3 epilayers grown on sapphire substrate by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition"
- Conductive β-Ga2O3 epilayers grown on the sapphire substrate using metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) were studied by Si-ion implanted.
- A metal-insulator-semiconductor diode (MISD) was fabricated using undoped and Si implanted β-Ga2O3 epitaxial layer..
- The electrical and carrier transport properties of the different MISD with different distance between cathode and anode contact ranging from 10 to 200 μm is studied.
- A reverse breakdown voltage of about 1.1 kV was observed in case of anode-cathode distance of 200 μm.

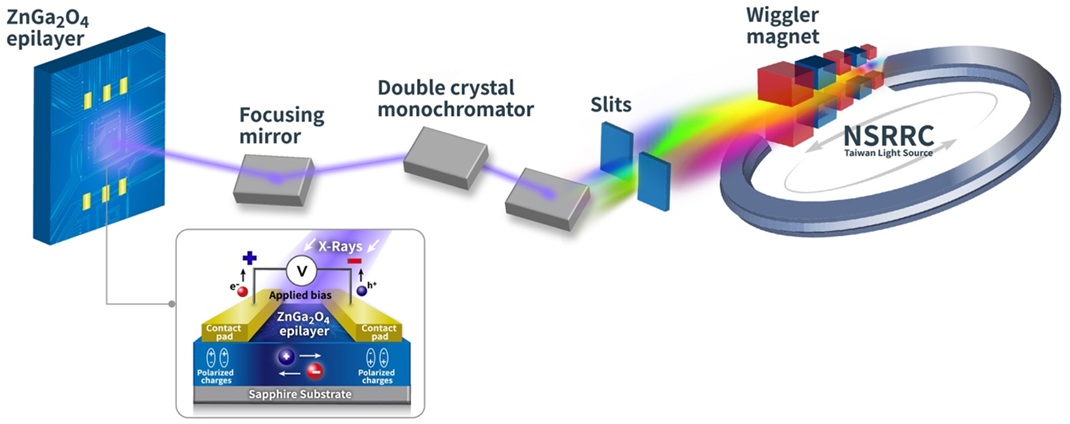
"Direct hard X-ray photodetector with superior sensitivity based on ZnGa2O4 epilayer grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition"
- Fabricated a highly sensitive direct irradiating X-ray photodetector (DXPD) based on Zinc Gallium Oxide (ZnGa2O4) epilayers with a metal-semiconductor-metal structure.
- The effect of changing the applied bias voltage on the time response of the DXPD was investigated.
- ZnGa2O4 based detectors also exhibited remarkable sensitivity of 2.87 × 109 μC Gyair−1cm−2 for the incident flux of 5.7✕107 counts/sec at 15 V.
- It can be concluded that ZnGa2O4 epilayers grown by MOCVD hold immense potential for use in high-performance hard XPDs.

"Cubic phase optimization and influence of post-annealing on microstructure, optical, wetting, and nanomechanical properties of zirconia thin films"
- The X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectra of zirconia films annealed at 500 °C reveal the formation of stable cubic phase with a crystallite size of 10.7 ± 0.8 nm at room temperature.
- Optical transparency of the zirconia film annealed at 500 °C is high, approaching 80% in the visible range.
- The post-annealing temperature influences provide a method for tuning the optical, wetting and mechanical characteristics of zirconia thin film.
- The post-annealing temperature strongly influences the characteristics of zirconia film, which can provide a method for tuning the optical, wetting, and mechanical properties of the zirconia film.


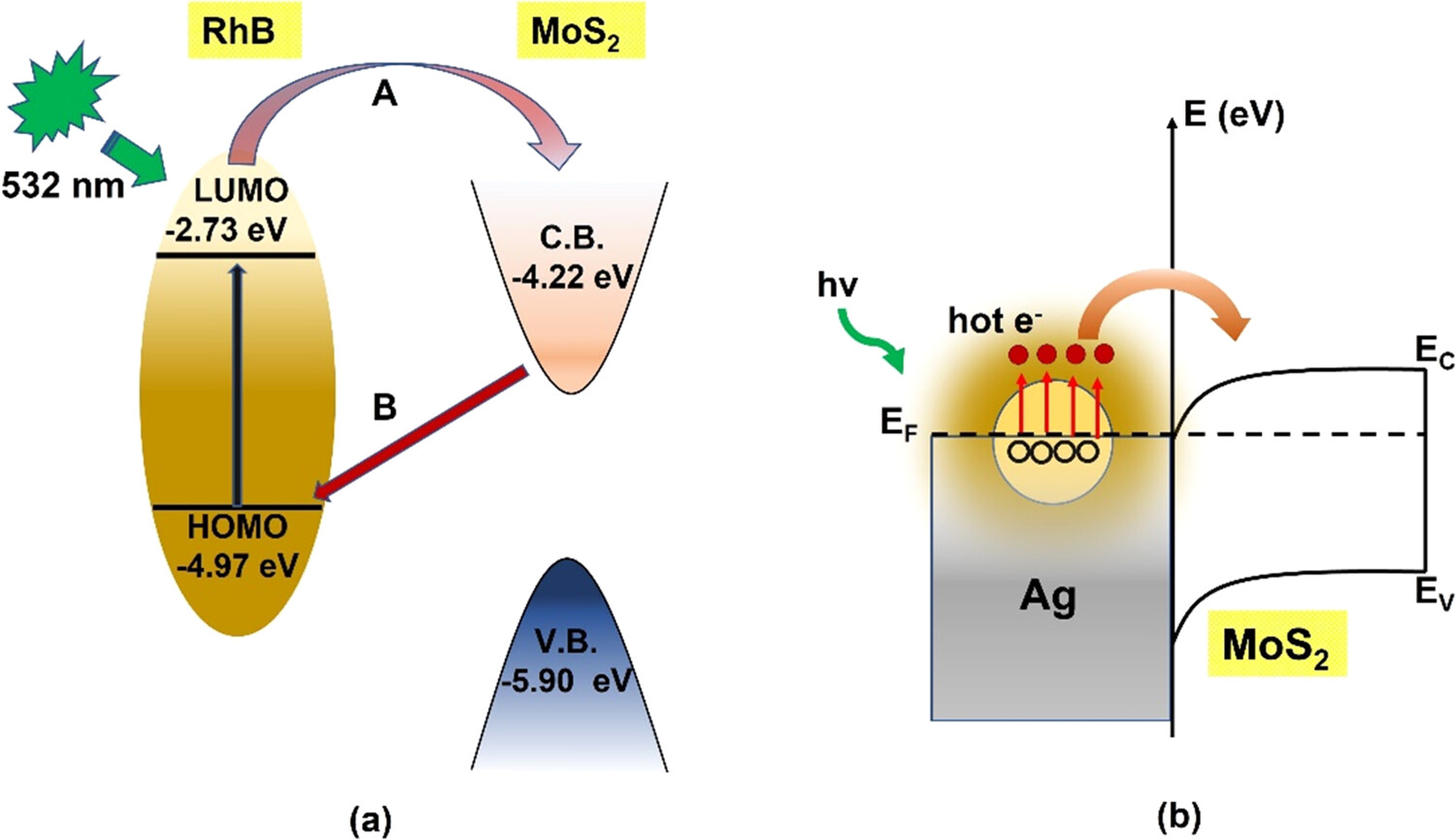
"MoS2−AgNano composite-Based SERS Substrates with an Ultralow Detection Limit"
- The SERS substrate prepared with the nanoplate morphology MoS2 structures shows excellent detection up to 10–9 M concentration of rhodamine B (RhB) dye.
- MoS2 nanoplates have been functionalized with Ag nanoparticles (NPs) to optimize the MoS2 SERS performance.
- The MoS2–Ag nanocomposite SERS substrates successfully detect an ultralow concentration of 10–15 M of RhB dye with an enhancement factor of 9.2 × 107.
- A charge transfer mechanism between RhB molecules and MoS2 is proposed along with the contribution of Ag NPs in ultralow SERS detection.
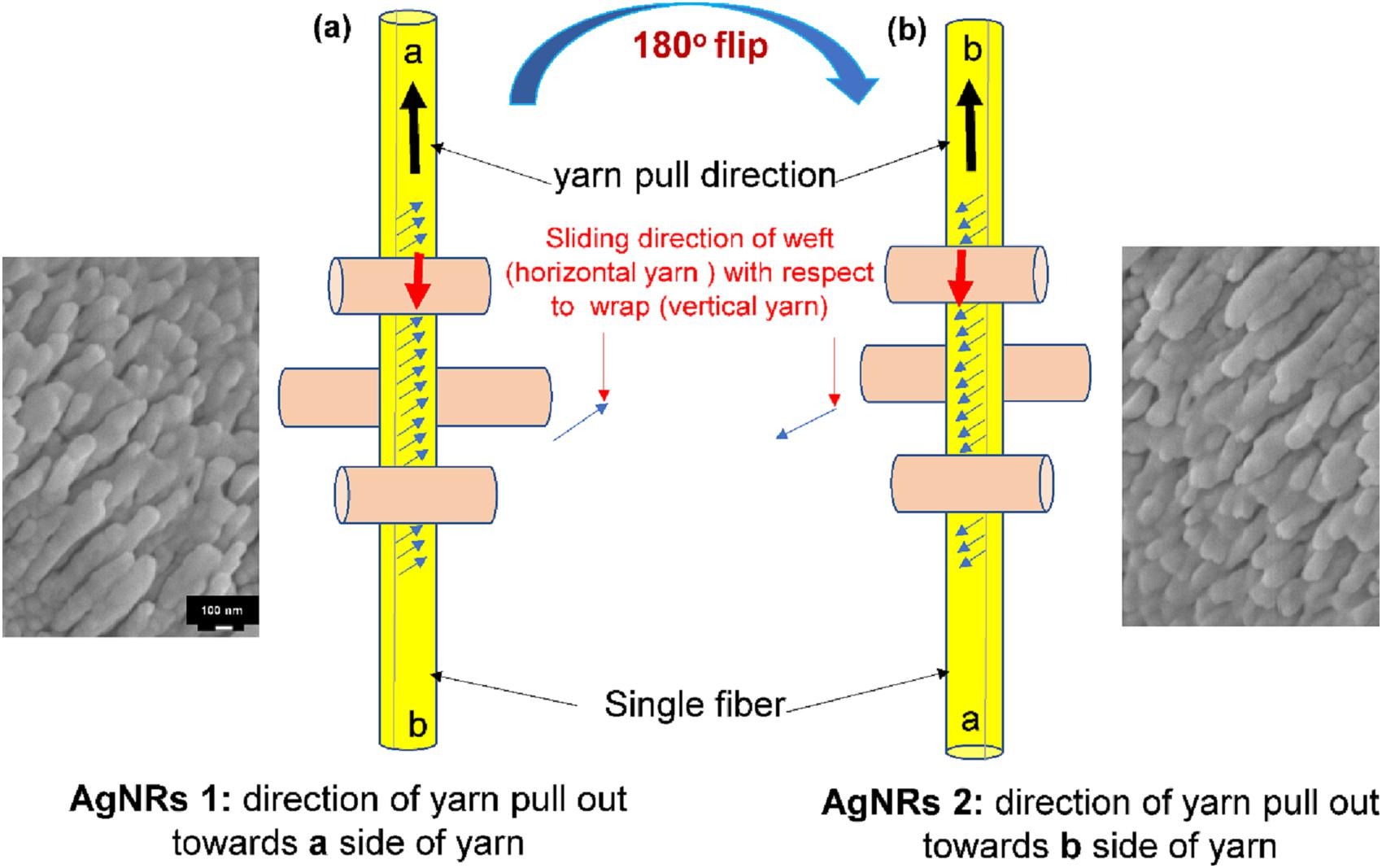
"Investigating the effect of aligned Ag nanorods on para-aramid woven fabric and anisotropy in inter-yarn friction"
- Inter yarn friction, measured in terms of yarn pull-out force, is a major mechanism of energy absorption in soft body armor.
- Increasing inter-yarn friction of para-aramid fabric to improve ballistic performance without adding weight is challenging.
- The AgNRs-coated para-aramid fabric retains its flexibility and weight while increasing yarn pull-out force by 130%.
- The numerical model confirms the experimental results that formation of nanorods significantly increases inter-yarn friction and pull-out force.

"Recent Advances and Challenges in Textile Electrodes for Wearable Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review"
- The transition from wet Ag/AgCl electrodes to various types of gel-free dry electrodes has made it possible to continuously and accurately monitor the biopotential signals.
- There has been a significant advancement in the fabrication of wearable conductive textile electrodes for monitoring biopotential signals.
- The advantages and limitations of various types of textile electrodes are discussed, and key challenges and future research directions are identified.
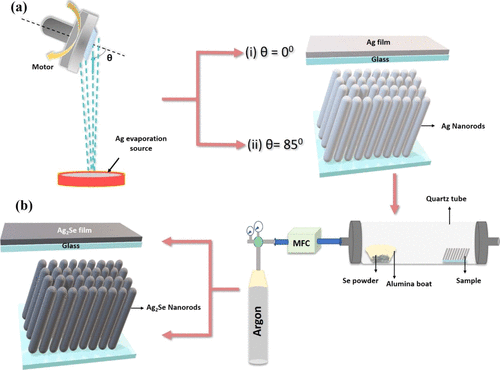
"Ag2Se Nanorod Arrays with Ultrahigh Room Temperature Thermoelectric Performance and Superior Mechanical Properties
"
- We report the fabrication of Ag2Se nanorod arrays by glancing angle deposition technique (GLAD) followed by simple selenization in a two-zone furnace.
- The superior thermoelectric performance of Ag2Se nanorod arrays compared to planar Ag2Se films could be ascribed to the unique nanocolumnar architecture that not only facilitates efficient electron transport but also significantly scatters phonons at the interfaces.
- the nanoindentation measurements were performed to explore mechanical properties of the as-prepared films.